Infection control is a critical component of care for patients in Intensive Care Units (ICUs). Due to the vulnerability of ICU patients, who often have weakened immune systems or are undergoing invasive procedures, implementing proper infection control measures is essential for their safety and recovery. This article will explore key infection control practices that healthcare professionals follow to ensure the well-being of ICU patients.
Hand Hygiene: The Foundation of Infection Control
The most effective way to prevent the spread of infections is through proper hand hygiene. Healthcare workers and visitors must wash their hands thoroughly before and after interacting with an ICU patient. Hand sanitizers with at least 60% alcohol can also be used when soap and water aren’t available.
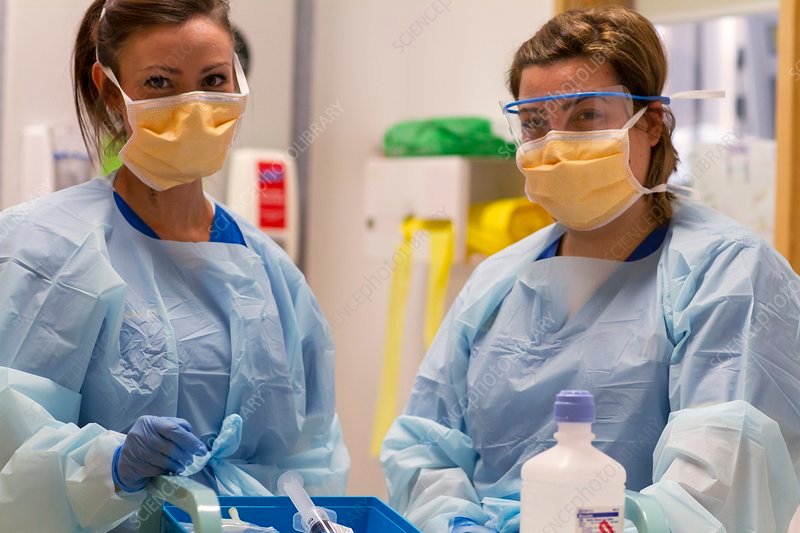
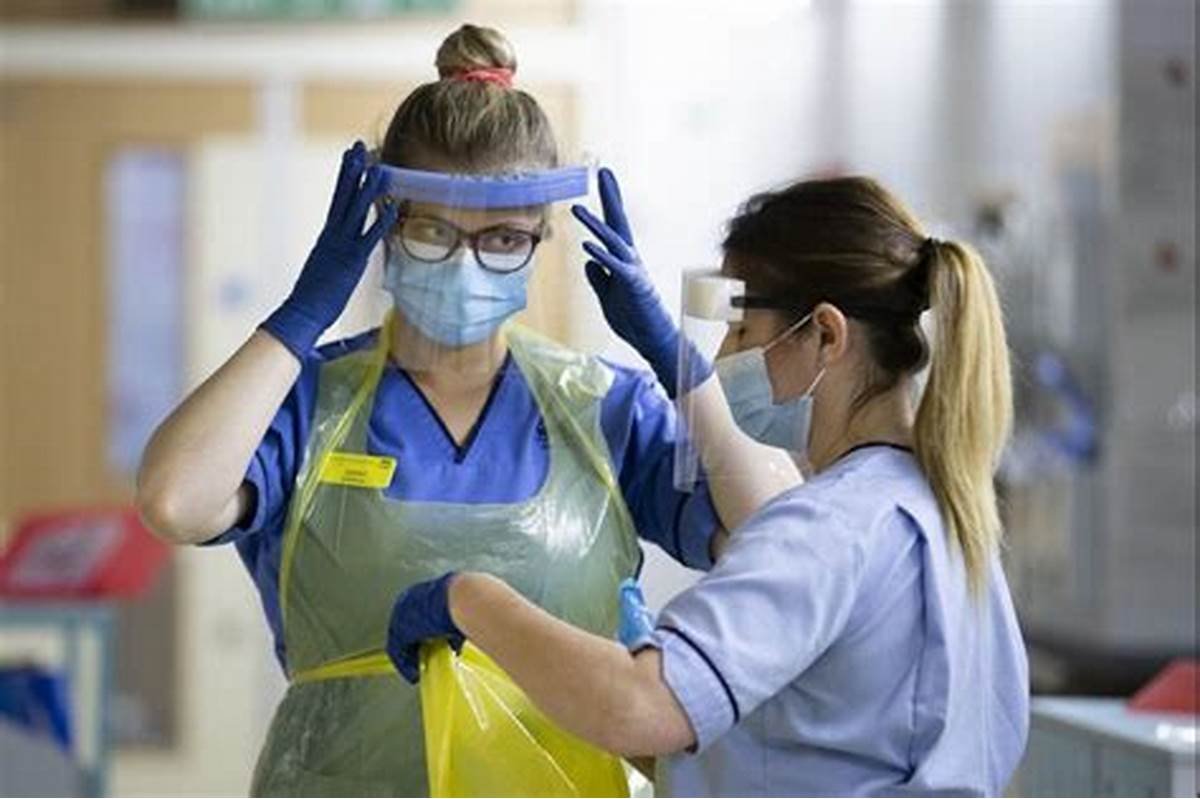
Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is vital in preventing the transmission of infectious agents. Healthcare professionals must wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, gowns, masks, and face shields, depending on the situation and the patient’s condition. This ensures that both the patient and healthcare providers are protected from potential infections.
Sterile Techniques for Procedures
Many procedures in the ICU require sterile techniques to reduce the risk of infection. Healthcare providers must follow strict protocols when inserting intravenous lines, catheters, or performing surgeries. Sterile gloves, sterile drapes, and antiseptic solutions are commonly used to maintain a clean environment.
Environmental Cleaning and Disinfection
Regular cleaning and disinfection of the ICU environment are crucial to preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). High-touch surfaces, such as bedrails, light switches, and doorknobs, should be cleaned and disinfected frequently using hospital-grade disinfectants. This reduces the chance of bacteria or viruses lingering in the patient’s immediate environment.

Antibiotic Stewardship
Antibiotic stewardship involves using the right antibiotic at the correct dose for the right duration. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics in ICU patients can lead to antibiotic-resistant infections. Careful monitoring and decision-making regarding the use of antibiotics help reduce the risk of resistant infections and improve patient outcomes.
Infection Surveillance
Constant monitoring and surveillance of ICU patients are necessary to detect infections early. Healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of infection, including fever, changes in vital signs, or wound drainage. Regular lab tests, including blood cultures and urine tests, can help identify infections before they become serious.
Patient Isolation for Contagious Diseases
In cases where a patient has a contagious infection, isolation protocols should be followed to prevent the spread of the disease to other patients. Isolation can include placing the patient in a private room, using dedicated medical equipment, and limiting visitor access.
Conclusion
Infection control is vital in the ICU to protect vulnerable patients and prevent the spread of infections. By following proper hygiene practices, using PPE, maintaining a sterile environment, practicing antibiotic stewardship, and conducting diligent surveillance, healthcare professionals ensure that ICU patients receive the safest and most effective care possible.