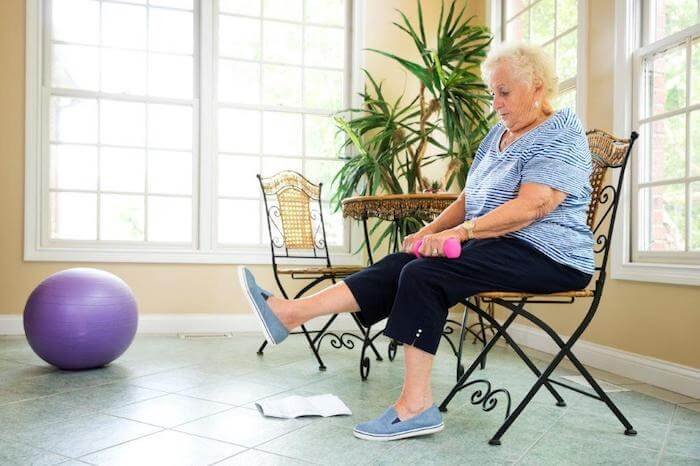
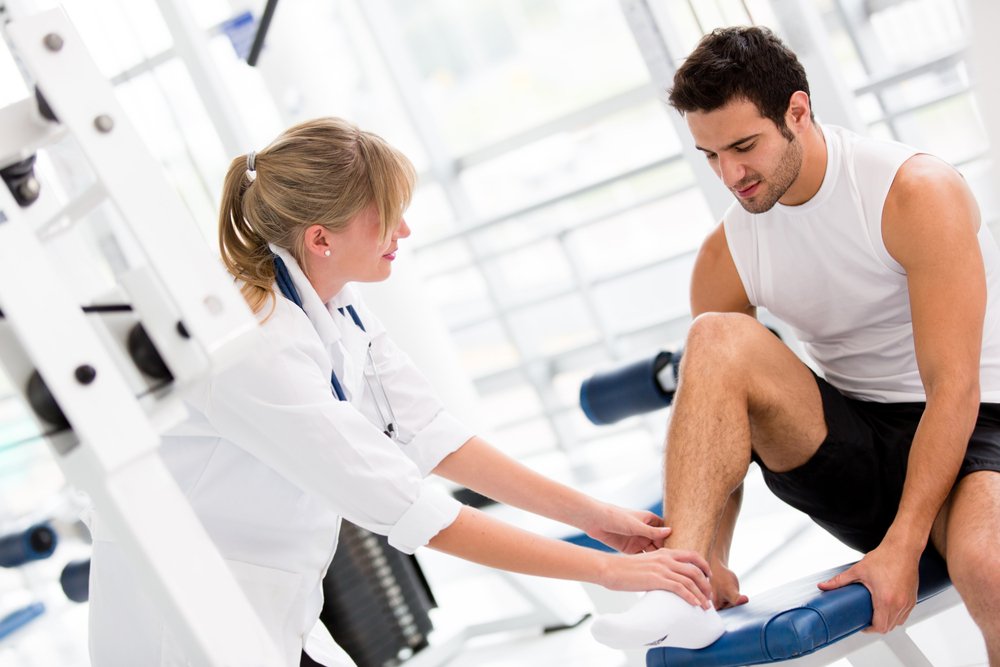
Occupational therapy (OT) plays a vital role in rehabilitation by helping individuals regain the skills needed for daily life after an injury, illness, or surgery. OT focuses on improving a person’s ability to perform tasks such as dressing, cooking, working, and participating in leisure activities. The goal of occupational therapy is to help people live as independently and fully as possible, regardless of the challenges they face. In this article, we’ll explore the role of occupational therapy in rehabilitation, how it benefits patients, and why it’s an essential part of recovery.
1. What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy is a type of rehabilitation therapy that focuses on helping individuals regain the skills necessary to perform daily tasks and activities. OT addresses both physical and mental aspects of recovery, as it can be used to improve motor skills, cognitive abilities, and emotional well-being. Occupational therapists work with patients who have injuries, disabilities, or illnesses that affect their ability to function independently.
Occupational therapy may include:
- Training in fine motor skills for tasks like writing, buttoning shirts, or using utensils
- Helping individuals adapt their living environment to meet their needs
- Developing strategies for managing tasks at work or school
- Addressing emotional challenges related to disability or injury
OT ensures that individuals can perform daily tasks more easily, improving their overall quality of life.
2. Restoring Independence After Injury or Illness
One of the key roles of occupational therapy in rehabilitation is helping individuals regain their independence after an injury or illness. For example, if a person has suffered a stroke, they may experience difficulty with basic tasks like dressing, eating, or bathing. An occupational therapist will work with them to improve their ability to perform these tasks independently. This may involve exercises to strengthen muscles, teaching new techniques, or recommending adaptive equipment.
How OT restores independence:
- Providing training in adaptive techniques to complete tasks more easily
- Introducing assistive devices (e.g., grab bars, modified utensils) to support daily activities
- Developing motor skills and coordination to improve movement and function
- Helping patients regain the ability to complete tasks at home, work, or school
By restoring independence, OT enhances a person’s confidence and empowers them to take control of their life again.
3. Adapting Environments for Better Functioning
A key aspect of occupational therapy is helping individuals adapt their living and working environments to better suit their needs. People recovering from an injury, surgery, or illness may struggle to navigate their environment due to mobility issues or limited physical abilities. Occupational therapists assess these environments and recommend modifications that can make tasks easier and safer.
Examples of environmental adaptations include:
- Installing ramps, handrails, or wider doorways to accommodate mobility devices
- Adjusting furniture or home layouts to reduce strain and improve accessibility
- Recommending adaptive tools (e.g., reaching devices, special keyboards) to assist with everyday tasks
- Modifying workspaces to help individuals return to work or school
These adaptations enable individuals to live and work more comfortably, reducing frustration and enhancing their overall well-being.
4. Addressing Cognitive and Emotional Challenges
In addition to improving physical abilities, occupational therapy also addresses cognitive and emotional challenges that may arise after an injury or illness. People recovering from a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or mental health issue may have difficulty concentrating, remembering things, or managing emotions. Occupational therapists work with patients to develop strategies to overcome these challenges, improving their ability to function at home and in social situations.
How OT helps with cognitive and emotional challenges:
- Improving memory and attention through cognitive exercises and techniques
- Teaching emotional regulation strategies to cope with stress, anxiety, or depression
- Using mindfulness and relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety and improve focus
- Encouraging participation in social activities to enhance mental health and well-being
By addressing both cognitive and emotional aspects of recovery, OT helps individuals regain their mental and emotional health, which is crucial for overall rehabilitation.
5. Supporting Return to Work or School
Returning to work or school after an injury, illness, or surgery can be a challenging process. Occupational therapists play a vital role in helping individuals re-enter the workforce or resume their studies by offering strategies and training to adjust to new limitations. OT can help individuals learn new skills, adapt to a modified workspace, or adjust their schedule to meet their needs.
Support OT provides for work or school:
- Assessing the workplace or school environment for necessary adaptations
- Recommending tools and equipment to improve productivity and reduce strain
- Teaching strategies for managing work or school tasks despite physical limitations
- Supporting social interactions and teamwork in a work or school setting
Occupational therapy helps individuals return to work or school with confidence, promoting a sense of purpose and achievement.
6. Preventing Future Injuries and Complications
Occupational therapy also focuses on preventing future injuries and complications by teaching patients how to protect their bodies and maintain good habits. For example, an occupational therapist may teach proper posture or ergonomic techniques to reduce the risk of strain or injury during daily activities. This proactive approach ensures long-term recovery and helps individuals stay healthy and independent.
Preventative strategies in OT include:
- Teaching proper body mechanics to avoid strain or injury
- Providing exercises to maintain strength, flexibility, and balance
- Educating patients about self-care routines to prevent further injury
- Offering advice on injury prevention for high-risk individuals (e.g., athletes, elderly)
By focusing on prevention, occupational therapy helps individuals avoid setbacks and maintain their recovery progress.
7. Improving Quality of Life and Well-Being
Ultimately, the role of occupational therapy in rehabilitation is to improve a person’s overall quality of life. OT helps individuals regain independence, adapt to challenges, and participate in activities that bring them joy and fulfillment. By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of recovery, occupational therapy promotes a well-rounded and healthy lifestyle.
How OT improves quality of life:
- Supporting daily activities such as eating, bathing, and dressing with ease
- Enhancing social interactions and participation in hobbies or leisure activities
- Improving self-confidence and emotional well-being through recovery
- Encouraging a more active and engaged lifestyle
Occupational therapy empowers individuals to live a fuller life, regardless of the obstacles they may face.
Conclusion
The role of occupational therapy in rehabilitation is crucial for helping individuals regain independence, improve daily functioning, and enhance their overall quality of life. Whether through physical exercises, environmental modifications, cognitive support, or emotional guidance, occupational therapy addresses the whole person. By providing tailored interventions that promote recovery and prevent future complications, occupational therapy helps individuals overcome challenges and lead more independent and fulfilling lives. If you or a loved one is recovering from an injury, illness, or surgery, occupational therapy can play an essential role in the healing process.